Electric stimulation therapy machines have become popular tools in both home and clinical settings for managing pain, improving recovery, and stimulating muscles. Among the most common technologies are TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation). While they may look similar on the surface—and even share some features—their purposes, effects, and benefits are quite different. In this article, we’ll break down the differences between EMS and TENS units, compare their uses, advantages, and limitations, and help you decide which electric muscle stimulator is right for your needs.
Understanding Electric Stimulation Therapy
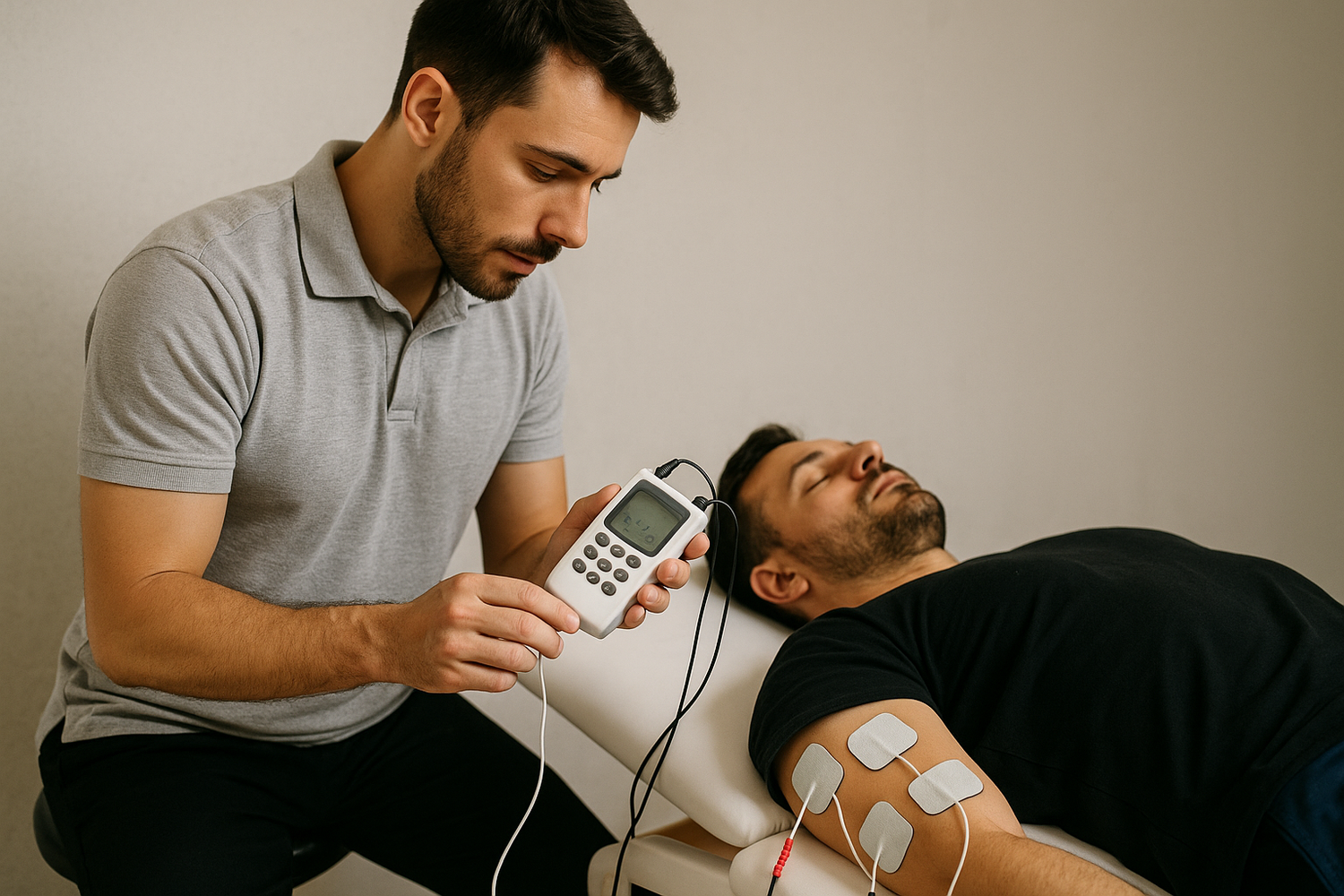
Electric stimulation therapy machines work by sending electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin. These impulses either stimulate nerves or muscles, depending on the type of machine being used.
There are two primary types of therapy equipment for this purpose:
- TENS units are designed to relieve pain by blocking pain signals sent to the brain.
- EMS machines, on the other hand, are built to contract muscles, mimicking the body's natural signals to improve muscle tone and strength.
Both devices fall under the umbrella of electrotherapy, and while they may look alike and even share overlapping features, their applications and effects are quite different.
What is a TENS Unit?
A TENS unit (short for Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) is a pain relief device that uses low-voltage electrical current to disrupt pain transmission. It’s commonly used for:
- Chronic pain
- Back pain relief
- Arthritis
- Neck pain
- Muscle spasms
The electrode pads are placed on or near the area of discomfort. When activated, the stimulator sends electrical impulses to the nerves, helping to “confuse” or override pain pathways.
Advantages of Using TENS
- Provides temporary pain relief without medication.
- Non-invasive and portable for pain therapy on the go.
- Ideal for treat pain from a wide range of conditions.
- Customizable with multiple modes and intensities.
Limitations of TENS
- Offers no direct muscle stimulation.
- Pain relief may vary depending on the individual.
- Not effective for improving muscle strength or tone.
Popular settings may include 20 intensities or even 24 modes, depending on the tens machine used. Some models, such as a dual channel TENS EMS unit, provide extra versatility.

What is EMS?
EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation), also referred to as NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation), works differently. Instead of targeting nerves to reduce pain, EMS targets muscle tissue to contract and relax muscles. The goal? Muscle development, toning, recovery, and rehabilitation.
EMS is commonly used for:
- Muscle therapy after surgery or injury
- Preventing or reducing muscle atrophy
- Enhancing muscle recovery
- Increasing muscle strength or endurance
Advantages of EMS
- Promotes muscle strength and recovery.
- Supports rehabilitation and improve muscle tone.
- Helps maintain muscle mass in those with limited mobility.
Limitations of EMS
- Not intended for pain management.
- Can feel intense or uncomfortable at higher settings.
- Improper use may lead to muscle fatigue or soreness.
Some EMS devices are also used in cosmetic settings to promote better posture or stimulate facial muscles, although their clinical value varies.
EMS vs. TENS: Key Differences
| Feature | TENS Unit | EMS Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Pain relief therapy | Muscle stimulation |
| Target | Nerve stimulator | Muscle stimulator |
| Conditions Treated | Chronic pain, arthritis | Muscle atrophy, weakness |
| Sensation | Tingling without movement | Muscle contraction and pulsing |
| Main Application | TENS therapy for pain relief | Muscle therapy and strengthening |
| Use in Recovery | Helps treat pain post-injury | Supports rehabilitation |
| Common Modes | 12–24 modes for tens for pain | Strengthening, toning programs |
| Common Form Factor | Portable pain relief units | Often part of massage machine |
| Customization | Dual channel with 8+ pads | Pulse muscle stimulator with variable intensity |
Which electric stimulation therapy machine should you choose?
Use a TENS Unit If:
- You suffer from chronic back, neck, or joint pain.
- You need a portable pain relief solution for everyday use.
- You’re recovering from an injury and need temporary pain relief.
- You prefer non-pharmaceutical options for pain management.
Choose EMS If:
- You are recovering from muscle injury or muscle atrophy.
- You’re looking to enhance muscle strength, tone, or muscle recovery.
- You're dealing with spasms or require neuromuscular re-education.
- You want to maintain muscle health during inactivity or post-surgery.
In some cases, a 3-in-1 TENS unit or dual channel EMS muscle stimulator can offer both functionalities in one therapy machine for pain and muscle use.
What About Cost?
Both EMS and TENS devices are available in a wide price range, depending on features, number of modes, electrodes, and whether they are wireless or not.
- Basic tens unit muscle stimulator: $30–$80
- Advanced electric muscle stimulator (EMS): $50–$150
- Combined ems tens models: $80–$200+
Wireless TENS units, rechargeable electric machines, and pulse massager with 24 modes can drive up the price, but offer more flexibility and better battery life.
Also consider how many 8 reusable electrode pads are included, how many intensities for gradual stimulation are offered, and if accessories like pads for back, straps, or foot massagers are part of the package.
EMS and TENS: A Powerful Combo?
While they serve different purposes, many electronic muscle stimulation devices now combine EMS and TENS capabilities. These hybrid units are ideal for users who want:
- Pain relief and muscle stimulation in one session
- Full-body support: back, shoulder, leg, neck
- Flexibility with portable dual channel options
- Multi-goal therapy, like relieving pain and improving muscle
Just be sure to follow instructions closely to avoid overstimulating sensitive areas. Always consult with a healthcare provider if you’re managing specific conditions.
Who Should Avoid Electric Stimulation Therapy Machine?
Though generally safe, individuals with pacemakers or serious heart conditions should not use EMS or TENS units without medical approval. Also, pregnant women should avoid using stimulation devices on the abdomen or lower back.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re managing chronic pain, rebuilding after injury, or looking to enhance muscle therapy, electrical stimulation can be a game-changer. Understanding the distinction between EMS and TENS therapy ensures you get the most out of your stim machine and avoid ineffective or even counterproductive treatments.
A tens unit for pain relief can significantly improve your quality of life, while an EMS machine supports muscle strength and recovery. When used properly, both tools offer a safe, drug-free path toward better well-being.
The Electric pumice for skin renewal is your reliable assistant in skin care, which will help you achieve smoothness and youth. Turn routine procedures into fun and enjoy visible results after the first applications! You can buy this device at the best price in our store.
Key Takeaways
- TENS is best for temporary pain relief and pain management.
- EMS helps with muscle stimulation, recovery, and preventing muscle atrophy.
- Devices often offer dual channel functionality and multiple modes for customization.
- Prices range based on features like wireless, rechargeable electric, or 8 reusable electrode pads.
- Combining electric pulse massager features can provide both therapy and recovery in one unit.
When choosing your next therapy machine for pain, think about your needs, goals, and physical condition. Whether you need a pulse massager muscle stimulator for your shoulders or a massager machine for your legs, there’s a solution out there to help you relieve pain, recover faster, and live more comfortably.











Hinterlasse einen Kommentar
Diese Website ist durch hCaptcha geschützt und es gelten die allgemeinen Geschäftsbedingungen und Datenschutzbestimmungen von hCaptcha.